When patients’ lung function
continues to decline
SUSPECT
PULMONARY
FIBROSIS

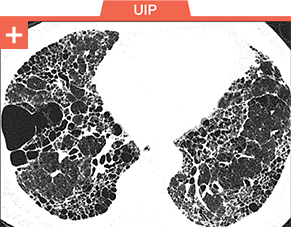
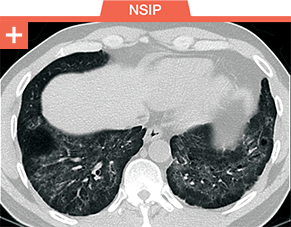
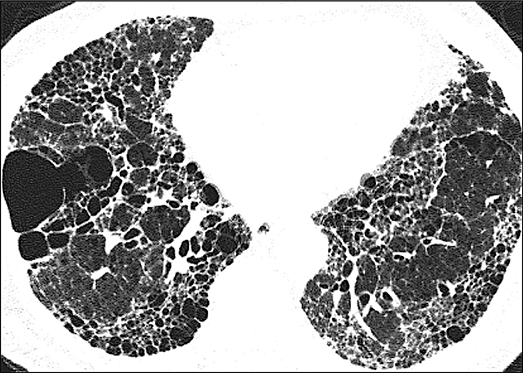
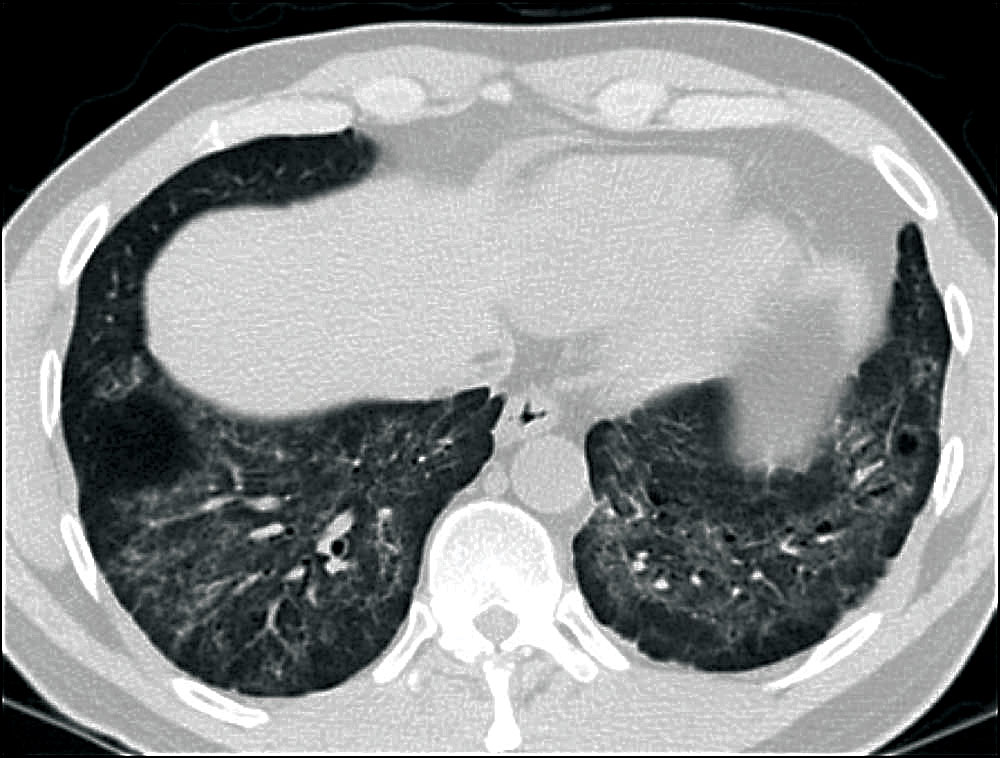
Pulmonary fibrosis is a common threat across a wide range of ILDs, including
autoimmune ILDs, that may lead to irreversible harm and early mortality1-6
FOLLOW the PATH. SCROLL TO SEE THE SIGNS